DeFi Trading Explained: How to Trade in Decentralized Finance
Welcome to the Future of Trading
DeFi trading (Decentralized Finance) lets you swap cryptocurrencies directly with other users through smart contracts. No banks, no brokers, just you, your wallet, and automated code handling the trades.
DeFi trading didn't evolve from banking; it was engineered as its antithesis.
While traditional exchanges were busy adding more middlemen, fees, and "user-friendly" restrictions, a group of crypto rebels decided to throw out the entire playbook.
Instead of being a passive spectator watching your trades get processed by someone else's system, you become an active participant in the market itself.
Yes, it takes a bit more effort to understand, but the rewards include true asset ownership, transparent pricing, and access to financial instruments that simply don't exist in traditional finance.
Once you experience true financial sovereignty-even just once-going back to asking permission for your own money feels absurd.
What This Complete DeFi Trading Guide Covers
How DeFi actually works - Skip the theory and understand what happens when you click "swap" on Uniswap.
Platform breakdown - Which DEXs, Layer 2s, and other platforms to use for different trading strategies.
Your first trade walkthrough - Step-by-step setup from wallet creation to executing your first swap safely.
Advanced strategies that work - Flash loans, yield farming, and cross-chain arbitrage explained practically.
Risk management essentials - How to avoid expensive mistakes and protect your funds in an unforgiving environment.
What Is DeFi Trading?
DeFi or Decentralized Finance can be defined as financial services built on blockchain technology that operate without traditional intermediaries like banks or brokers.
DeFi trading covers everything from simple token swaps to complex derivative strategies, all happening through smart contracts instead of traditional brokers.
The simplest form is spot trading - swapping one token for another using automated market makers. But you can also trade perpetual futures, provide liquidity to earn fees, or even create synthetic exposure to real-world assets.
The core difference is that you're interacting directly with protocols rather than placing orders through a company's platform. When you trade on Uniswap, you're swapping against liquidity pools funded by other users.
When you trade perps on GMX, you're betting against a decentralized pool of assets. When you lend on Aave, you're earning yield directly from borrowers.
Each trade happens through smart contracts that execute automatically based on predetermined rules.
No middleman processing your order, no company holding your funds, no customer service to call when things go wrong. The code handles everything, and since it's all on-chain, you can verify exactly what's happening with your money.
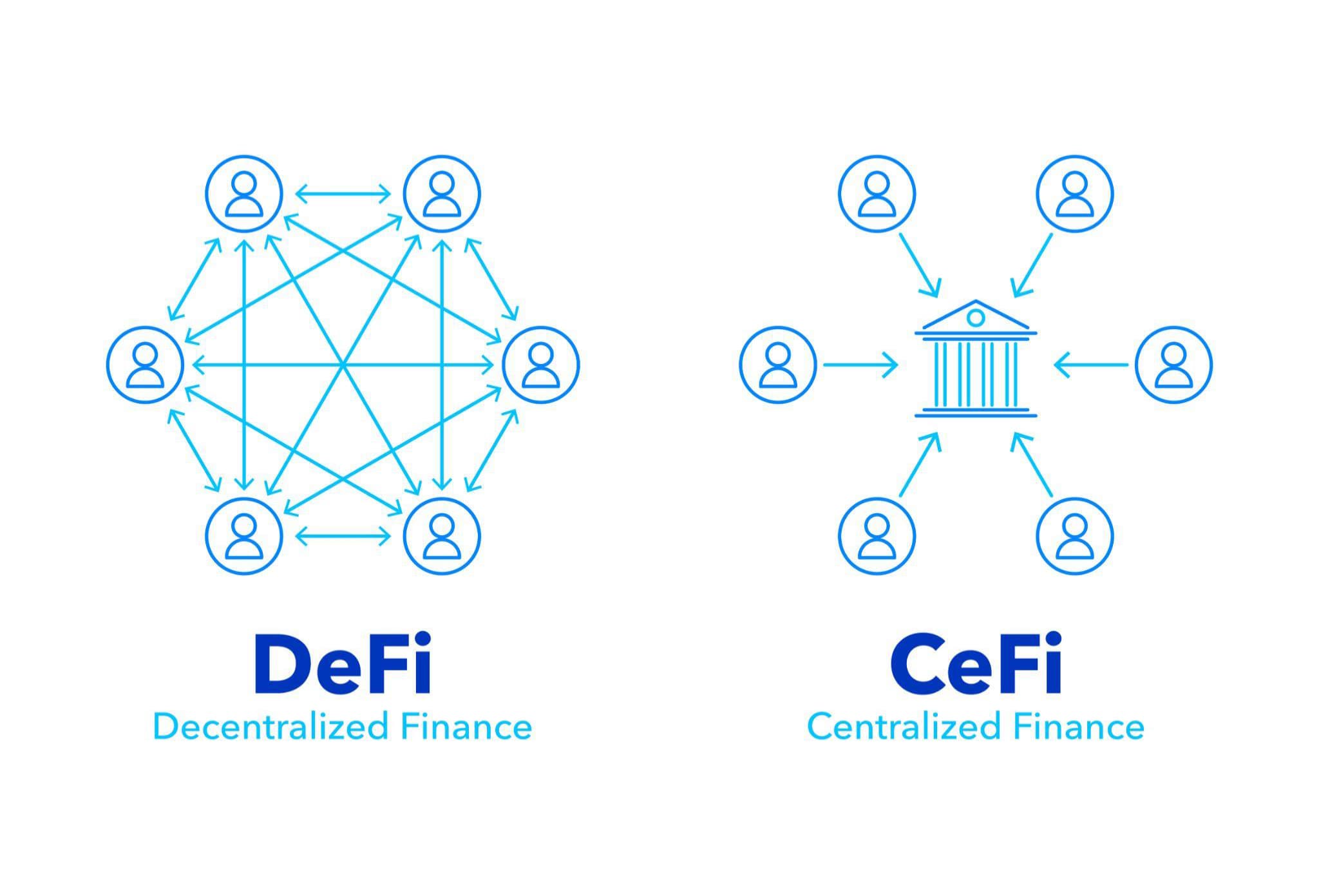
DeFi vs CeFi
Link Alt text: defi vs cefi concept
CeFi platforms like Binance and Coinbase still work like traditional brokers. They hold your money, process your trades, and can shut you down whenever they want.
DeFi protocols flip this completely by removing the middleman entirely.
Aspect | CeFi (Binance, Kraken, etc.) | DeFi (Uniswap, Aave, etc.) |
Control | Managed by centralized entities | Operates via smart contracts on blockchain, no central authority. |
Custody of Funds | Users deposit funds; the platform holds private keys. | Users retain full custody; funds are managed through wallets |
Trust Model | Trust is placed in the company or exchange to act honestly and securely. | Trustless – relies on blockchain consensus and code execution. |
Accessibility | Often requires KYC/AML checks, can be restricted by geography. | Open to anyone with internet access and a crypto wallet. |
Security Risks | Exchange hacks, insider fraud, mismanagement | Smart contract bugs, exploits, rug pulls. |
Regulation | Heavily regulated in most jurisdictions. | Operating in legal gray areas |
Products Offered | Spot & margin trading, lending, derivatives, staking, fiat gateways. | Decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending protocols, yield farming, synthetic assets, RWAs |
Fees | Platform sets fees (trading, withdrawal, etc.). | Gas fees (network dependent) + protocol fees (usually lower than CeFi but can spike). |
Quick summary:
CeFi = More user-friendly, regulated, custodial, but requires trust in a central authority.
DeFi = Permissionless, transparent, and user-controlled, but riskier if you’re not familiar with blockchain and smart contract risks.
DeFi trading means swapping cryptocurrencies through smart contracts instead of through a company's order book. When you trade on Uniswap, there's no Uniswap Inc. processing your transaction—just code running on Ethereum that automatically handles the swap based on mathematical formulas.
The liquidity comes from other users who've deposited their tokens into pools and earn fees when trades happen. So instead of trading against a company's inventory or other customers' limit orders, you're trading against these community-funded pools. The prices adjust automatically based on supply and demand within each pool.
Here's what makes it decentralized: no single entity controls the protocol, holds your funds, or can freeze your account. The smart contracts are publicly viewable code that executes exactly as written.
You connect your wallet, approve the transaction, pay the network fee, and the swap happens.
Read our complete guide to Cefi vs Defi here
The Technology Behind DeFi Trading
DeFi isn’t one piece of software, but rather a stack of technologies that work together.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on blockchains that automatically perform actions when specific conditions are met. In DeFi trading, they handle everything from token swaps to complex lending operations without requiring human oversight.
When you initiate a trade on a Dex, a smart contract verifies you have the tokens you want to swap, calculates the exchange rate, executes the trade, and transfers the new tokens to your wallet—all automatically. Once deployed, these contracts operate according to their programmed rules, which can only be changed through decentralized governance votes.
Modern smart contracts include sophisticated safety mechanisms, such as automatic pausing when unusual activity is detected and built-in slippage protection, to prevent users from receiving significantly fewer tokens than expected.
Learn more about Smart Contracts in our guide.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
AMMs replace traditional order book systems with mathematical formulas that determine token prices based on supply and demand within liquidity pools. Instead of matching buy and sell orders from different users, AMMs allow instant trading against these pools.
The most common AMM formula is x*y = k, where x and y represent the quantities of two tokens in a pool, and k remains constant. When someone buys Token A with Token B, the amount of Token A in the pool decreases while Token B increases, automatically adjusting the price according to this ratio.
Uniswap v4 introduced concentrated liquidity, allowing liquidity providers to focus their capital within specific price ranges for higher efficiency. Curve Finance optimized AMMs for similar-value assets like stablecoins, reducing slippage for these trades.
Liquidity Pools
Liquidity pools are smart contracts containing pairs (or groups) of tokens that enable trading on AMMs. Users deposit tokens into these pools and receive liquidity provider (LP) tokens representing their share of the pool.
Liquidity providers earn a portion of trading fees generated by the pool, but face impermanent loss risk when token prices diverge significantly from their initial ratio. For example, if you provide equal values of ETH and USDC to a pool, and ETH doubles in price, you'll end up with less ETH and more USDC than if you had simply held both tokens separately.
Advanced pools now support multiple assets, variable fees based on volatility, and integration with lending protocols to maximize capital efficiency.
Blockchain Networks and Layer 2 Solutions
Ethereum still remains DeFi's primary base layer, but now most trading volume has migrated to Layer 2 networks with faster transactions and lower fees while maintaining Ethereum's security guarantees.
Arbitrum and Optimism use optimistic rollups, processing transactions off-chain and periodically submitting batches to Ethereum. This reduces gas costs by 10-100x compared to mainnet Ethereum. Polygon operates as a side-chain with its own validators, offering even lower fees but with different security assumptions.
Solana’s high throughput with sub-second finality makes it popular for high-frequency trading strategies. Each network has developed distinct DeFi ecosystems with specialized protocols and trading opportunities.
Cross-Chain Bridges and Interoperability
Cross-chain bridges enable asset transfers between different blockchain networks, expanding trading opportunities beyond single ecosystems. These protocols lock tokens on one chain and mint equivalent representations on another chain.
LayerZero and Thorchain cross-chain swaps allow users to trade assets across different networks without centralized exchanges.
However, bridges do have security risks as they hold large amounts of locked assets and have been targets for some of the largest DeFi exploits, including the $600+ million Ronin bridge hack and several other Wormhole incidents.
Recent improvements include time delays for large withdrawals, multi-signature requirements, and insurance protocols, but cross-chain operations still require careful risk assessment.
Decentralized Governance
DeFi protocols operate without traditional corporate structures. Instead, they use token-based governance, where holders vote on protocol changes, fee adjustments, and upgrade proposals. Governance tokens are created to represent voting power rather than ownership shares.
Participation rates typically range from 5-15% of token holders, with voting power often concentrated among large holders and teams. Successful governance requires balancing technical expertise with community input, and many protocols struggle with low engagement and potential plutocracy concerns.
Governance decisions can also impact token values and protocol functionality, so users should understand the governance structure of the protocols they interact with.
AI Integration in DeFi (DeFAI)
AI integration represents DeFi's newest frontier, with automated agents handling increasingly sophisticated financial operations. These systems go beyond simple smart contract automation to provide dynamic decision-making capabilities.
Current applications include automated liquidity management, where AI adjusts liquidity provision strategies based on market conditions and historical performance data. Yield optimization protocols use machine learning to identify and execute the most profitable farming strategies across multiple platforms automatically.
AI-powered risk management systems monitor protocol health, detect unusual patterns that might indicate attacks or exploits, and can trigger automatic protective measures. Some employ sentiment analysis of social media and news to inform trading decisions and risk assessments.
Advanced implementations include MEV (Maximum Extractable Value) strategies where AI bots identify and capture arbitrage opportunities faster than human traders, and dynamic fee adjustment systems that optimize protocol revenue based on market conditions.
Popular DeFi Trading Platforms and Protocols
Here's where the real action happens and what each platform actually does.
Major Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Uniswap dominates Ethereum-based trading with over $1 billion in daily volume. Its strength lies in simplicity. Connect wallet, select tokens, swap. The platform's liquidity depth means you can execute large trades without major price impact. Uniswap v4's concentrated liquidity features allow more efficient capital deployment for advanced users.
Curve Finance specializes in stablecoin and similar-asset trading, using optimized algorithms that minimize slippage when swapping between USDC, DAI, USDT, and other pegged assets. If you're frequently moving between stablecoins or wrapped versions of the same token, Curve typically offers the best rates.
PancakeSwap leads the Binance Smart Chain ecosystem, providing Uniswap-like functionality with dramatically lower transaction costs. The tradeoff is BSC's more centralized architecture, but for smaller traders, the fee savings often justify this compromise.
SushiSwap began as a Uniswap competitor but has differentiated through community governance and multi-chain deployment. It offers yield farming opportunities and has expanded to multiple networks, making it popular with users seeking additional earning opportunities beyond basic trading.
1inch functions as a DEX aggregator rather than operating its own pools. It splits your trade across multiple platforms to minimize costs and slippage. For larger swaps, 1inch often delivers better execution than trading on any single DEX directly.
Layer 2 and Alternative Networks
Most Ethereum DeFi activity now occurs on Layer 2 networks due to the mainnet's high gas costs:
Arbitrum has become the dominant Layer 2, with deep liquidity across major protocols and gas costs 10-50x lower than mainnet
Optimism offers similar benefits with a growing ecosystem focused on public goods funding
Polygon operates as a separate chain but provides the cheapest transactions, popular for smaller trades and experimental protocols
Alternative Layer 1 networks have built substantial trading ecosystems:
Solana enables high-frequency strategies impossible on other chains, with Jupiter leading DEX aggregation
Avalanche uses subnet architecture for specialized financial applications
Base (Coinbase's Layer 2) is attracting mainstream adoption with simplified onboarding
Specialized DeFi Protocols
Moving on from just spot trading opportunities, DeFi offers financial instruments unavailable in traditional markets:
Lending Platforms like Aave and Compound enable borrowing against crypto collateral. These platforms support leveraged trading strategies and offer unique features like flash loans—uncollateralized loans that must be repaid within a single transaction.
Derivatives Platforms
Hyperliquid operates as a fully on-chain perpetuals exchange on its own Layer 1 blockchain, offering up to 50x leverage with zero gas fees and sub-second finality
GMX offers perpetual futures with up to 50x leverage, backed by a multi-asset pool
Synthetix creates synthetic exposure to commodities, forex, and equities
Ribbon Finance provides automated options strategies for yield generation
Yield Aggregators like Yearn Finance and Beefy automatically optimize returns across multiple protocols, removing the complexity of manually managing positions across different platforms.
Platform Selection Strategy
Your platform choice should match your trading style and risk tolerance. Consider these factors:
Transaction costs vs. trade size: A $50 trade needs the cheapest execution possible, while a $50,000 trade can justify higher fees for better security and liquidity.
Liquidity depth: Higher volume platforms provide better price execution and lower slippage. Check recent trading volumes rather than total value locked, as TVL doesn't always correlate with trading activity.
Security track record: Established platforms with multiple audits and a trusted operational history generally pose lower smart contract risks than newer platforms with untested code.
How to Start DeFi Trading: Step-by-Step Setup
Getting started with DeFi trading requires more technical setup than centralized exchanges, but the process has become much more user-friendly. Here's how to get your first trade executed safely.
Choose a Web3 wallet. This is your gateway to DeFi. Well-known wallet options include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet, but there are plenty of others that traders actually use daily. Phantom is a favorite for Solana, Rabby has become popular for its multi-chain support, and Keplr is widely used in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Secure your seed phrase before doing anything else. Write down your 12-24 recovery words on paper and store them somewhere safe, not in a digital file or photo. This phrase is your only way to recover your wallet if you lose access. Anyone with these words controls your funds, so treat them like cash.
Fund your wallet. The most common way is to buy crypto on a centralized exchange (like Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken) and transfer it over. You can also use fiat on-ramps such as MoonPay or Ramp to go directly from a bank card into your wallet.
Whatever route you choose, make sure you hold a small amount of the chain’s native token, ETH for Ethereum, MATIC for Polygon, SOL for Solana, AVAX for Avalanche, since you’ll need it to pay gas fees.
Add network connections. Most wallets let you add different networks so you can trade across ecosystems. For example, you can configure MetaMask to work with Arbitrum, Optimism, or Avalanche in just a few clicks.
Extra security: browser extensions like Pocket Universe or Wallet Guard can flag suspicious transactions before you sign them, and hardware wallets (Ledger or Trezor) add another layer of protection if you’re moving larger amounts.
Connecting to DeFi Platforms
Once your wallet is set up, it’s time to plug into the DeFi ecosystem. Start by heading to the official site of your chosen platform. Always double-check the URL because phishing sites are one of the most common risks. Bookmark the real domains for DEXs you’ll use regularly.
Most platforms will have a “Connect Wallet” button in the top-right corner. Click it, select your wallet, and approve the connection.
If you’re moving across chains, make sure your wallet is set to the correct network you’re working in.
Your First DeFi Trade Walkthrough
Making your first trade in DeFi is simpler than it sounds once you’ve got your wallet connected. Here’s how it usually goes in practice:
1. Select a trading pair
Open your DEX of choice. If you’re not sure where the best price is, start with an aggregator such as 1inch or Matcha. Type in the tokens you want to swap, such as ETH to USDC.
2. Enter the trade amount
Input how much you want to swap. If you’re new, keep it small. Even experienced traders often do a $10 “test swap” before moving larger amounts.
3. Review swap details
Most DEXs will show you the expected exchange rate, price impact, and fees. Pay attention to the slippage tolerance setting. (see the note at the end of this section).
4. Approve token spending
The first time you trade a token, you’ll need to approve it for the smart contract. On Uniswap, for instance, this means clicking “Approve [Token]” and confirming in your wallet. You'll do the same for lending protocols like Aave or Compound before supplying collateral.
5. Confirm the transaction
Click “Swap,” then sign the transaction in your wallet. Check the gas fee carefully. Ethereum mainnet can be expensive, while Layer 2s are usually far cheaper. Solana and Avalanche offer near-instant confirmations at low cost.
6. Monitor completion
Your new tokens will appear in your wallet within seconds to a few minutes. If they don't show up right away, tools like DeBank or Zapper can help you verify balances across chains.
That’s it, you’ve executed your first DeFi trade. From here, you can explore other avenues, such as lending or even testing derivatives platforms like dYdX, but a simple token swap is the best way to get comfortable.
Note: Slippage & Price Impact - Slippage is the difference between the quoted price and the actual execution price. It happens because trades shift the ratio inside liquidity pools. Small trades usually have almost no effect, but large trades can move the market. This is known as price impact.
To manage this, you can set a slippage tolerance (e.g., 0.5%) that limits how much worse a trade can execute before it automatically cancels. For big orders, consider splitting them into smaller swaps to reduce the impact.
Advanced DeFi Trading Strategies
Once you’ve mastered basic swaps, DeFi opens the door to other strategies.
These more advanced approaches tap into the unique way DeFi protocols can be combined, letting you pull off financial moves that used to be strictly for the big players in trad finance.
Yield Farming with Dynamic Rebalancing
Yield farming remains a cornerstone of DeFi, but advanced traders go beyond static pool deposits.
Dynamic rebalancing involves shifting assets between liquidity pools based on real-time yield data and market conditions.
Tools like Yearn Finance or Beefy optimize this by automating reallocations to chase the highest APYs.
The trick? Monitor impermanent loss closely and use gas-efficient platforms to avoid eating into profits. Stay agile—pools with high yields often cool off fast.
Flash Loan-Powered Strategies
Flash loans let you borrow massive sums without collateral, as long as you repay within one transaction. Advanced traders use them for arbitrage, liquidations, or collateral swaps.
For example, you might borrow to buy an underpriced asset on Uniswap, sell it at a premium on SushiSwap, and repay the loan all in seconds. Platforms like Aave and dYdX make this accessible, but you’ll need coding chops or reliable scripts to execute flawlessly.
MEV and Front-Running Plays
Miner Extractable Value (MEV) strategies are about capitalizing on transaction ordering in blockchain mempools. Advanced traders use bots to front-run trades or back-run liquidations for profit.
Tools like Flashbots have made this more accessible, but it’s still a high-stakes game requiring deep blockchain knowledge. Ethical concerns aside, MEV is a reality.
Synthetic Asset Trading
Synthetic assets, like those on Synthetix or Mirror, let you trade tokenized versions of real-world assets on-chain.
Advanced traders pair synthetics with leverage to amplify returns or hedge against DeFi volatility. For instance, shorting a synthetic Tesla token while longing ETH can balance your portfolio.
The catch? Synth platforms often have complex fee structures, so crunch the numbers carefully.
Staking Derivatives for Liquidity
Liquid staking derivatives, like Lido’s stETH or Rocket Pool’s rETH, let you stake assets while keeping them tradable. Advanced traders use these in lending protocols like Compound to earn double yields—staking rewards plus lending interest.
You can also leverage staked derivatives as collateral for flash loans or margin trading. Just keep an eye on slashing risks and platform-specific quirks.
Cross-Protocol Yield Optimization
Newer protocols like Balancer v2 and Curve V3 allow for intricate pool compositions and fee structures. Advanced traders stack these with external strategies, like looping, essentially borrowing against deposited assets to reinvest or using vault aggregators to maximize returns.
It’s all about understanding how protocols work together. Pairing Curve’s stablecoin pools with Aave’s lending can juice returns, but missteps can amplify losses.
Risk Management in DeFi Plays
No strategy is bulletproof in DeFi’s wild west.
Use stop-loss tools where available, diversify across protocols to avoid single-point failures, and keep a chunk of your portfolio in stablecoins to seize sudden opportunities.
Gas fees can kill profits, so optimize for layer-2s or sidechains when possible. Always audit smart contracts or stick to battle-tested platforms. Rug pulls are rare, but when they happen, they are devastating.
These strategies demand technical know-how, constant market monitoring, and a stomach for risk. Start small, test rigorously, and never bet the farm. DeFi rewards the bold but punishes the careless.
Where to Go From Here
You now have the foundation to start trading in DeFi safely. Start small and build confidence with each successful transaction. Your first $20 swap on Uniswap teaches you more than reading another dozen articles.
Get comfortable with basic swaps, then explore lending or liquidity provision once you understand how gas fees and slippage affect your returns.
The advanced strategies we covered can wait until you've got the basics down cold.
DeFi moves fast, but the fundamentals stay consistent. Smart contracts execute trades automatically, liquidity pools provide the assets you swap against, and your wallet gives you complete control over the process. Everything else is just variations on these themes.
The technology will keep evolving, especially with AI integration, but the core advantage remains: you're trading directly with protocols instead of through intermediaries.
Continue your DeFi education with LearningCrypto's specialized tools. Our Market Analytics help you track real opportunities across protocols, while our AI tutors provide personalized guidance as you explore more advanced strategies.
Get started today and join traders who've already made DeFi part of their regular toolkit.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Cryptocurrency investments carry risk; you should always do your own research before making any investment decisions.